Data Types
In Kinetics Neo, thermoanalytical data of the following data types can be analyzed:
If the signal is imported in absolute units such as [mg] for TG, [mW] for DSC or [µm] for DIL, the relative unit [%] is calculated from the absolute signal and the initial sample mass or length that have to be entered during the import. The latter is important for signal types TGA, DIL and DSC, because the kinetic analysis of such data is based on the signals in relative units ([%], [mW/mg], [µV/mg]).
TG (Thermogravimetry)
Mass change, sometimes denoted as ∆m, mostly in units [%] or [mg]. TG data for a kinetic analysis typically shows the mass loss during decomposition of the sample leading to one or several mass loss steps. Exemplary import of TG data:
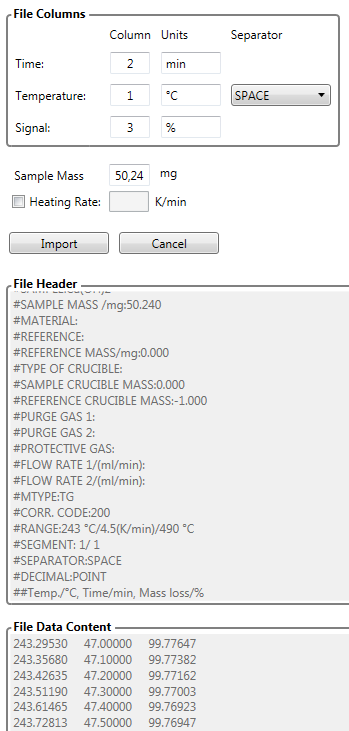
DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimetry)
Heat flow rate mostly in units [mW/mg], [mW], [µV] or [µV/mg]. DSC data for a kinetic analysis can for example show thermal effects (endo- and exothermic) during the decomposition of the sample or the curing effect which is exothermic. Exemplary import of DSC data:
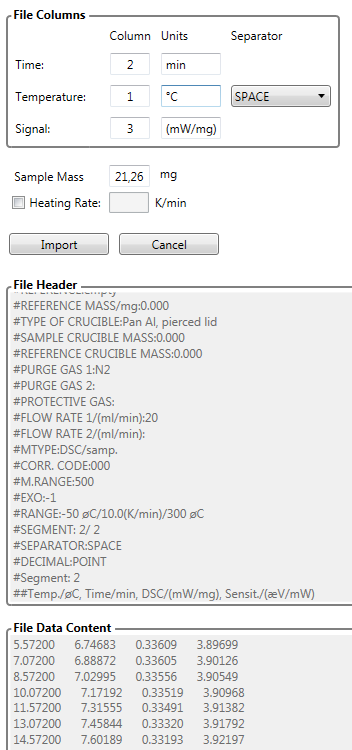
DSC Curing (Differential Scanning Calorimetry with Diffusion Control)
Heat flow rate mostly in units [mW/mg], [mW], [µV] or [µV/mg]. This signal type which is used for curing samples (exothermic effect) allows for incorporation and prediction of the glass transition temperature as a function of the conversion and time. Exemplary import of DSC Curing data:

DIL (Dilatometry)
Length change often denoted as dL/L0, dL or ∆L mostly in units [%] or [µm]. When for example ceramic samples are heated, the DIL signal typically shows an increase in sample length due to thermal expansion and decrease at high temperatures due to sintering (“sintering steps”). Kinetic analysis of the sintering can be done. Exemplary import of DIL data:
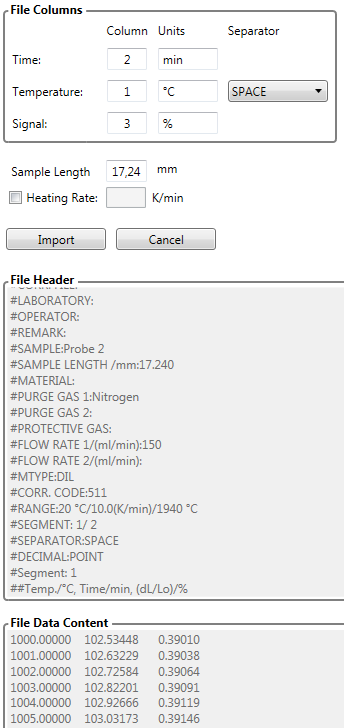
DEA (Dielectric Analysis)
Ion viscosity mostly in unit [Ohm·cm]. DEA data mostly show a significant increase in ion viscosity due to the curing effect. Exemplary import of DEA data:
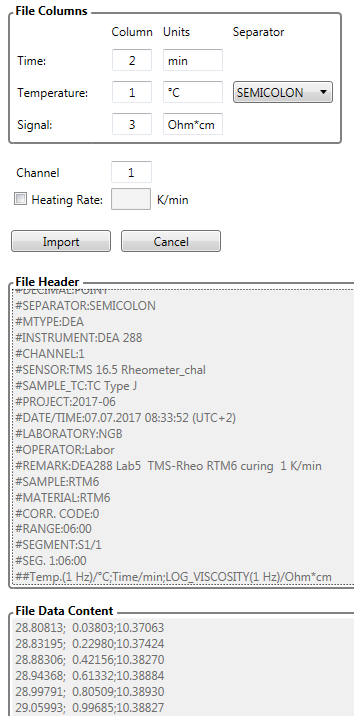
ARC Temperature (Accelerating Reaction Calorimetry)
The signal type has to be the sample temperature, mostly in unit [°C] or [K]. For example, exothermal reactions occurring during dynamic measurements lead to an extra increase in sample temperature. Exemplary import of ARC Temperature data:
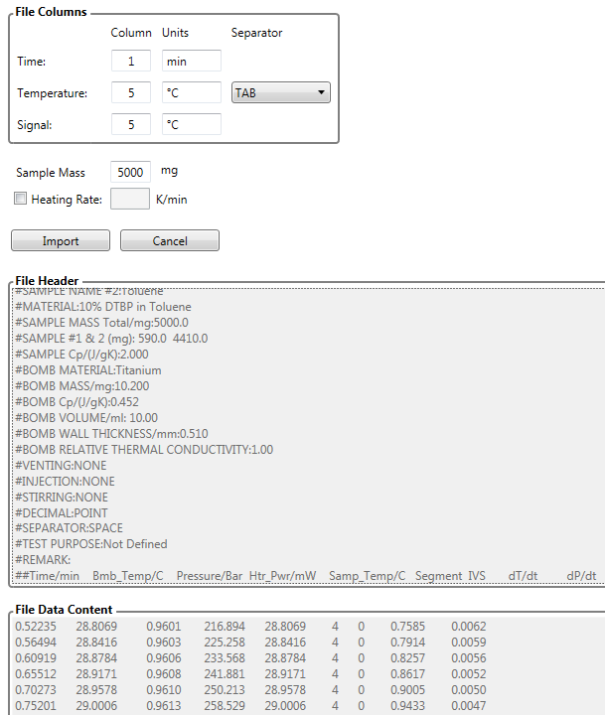
Viscosity
The data is mostly in unit log [Pa·s]. Viscosity data show for example a significant increase of the viscosity due to curing of the sample material. The viscosity can be measured either by a capillary rheometer (also known in literature as viscosimeter) or by a rotational rheometer (like Kinexus by NETZSCH). The data for Kinetics Neo are not the measured raw data, but already calculated viscosity values.
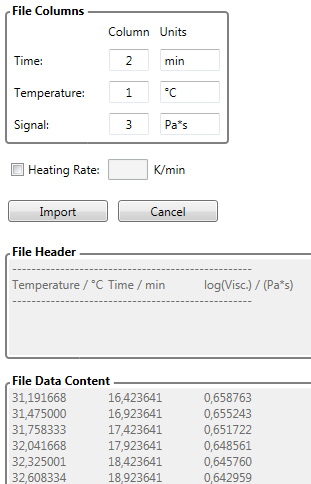
Rheometry (Torque)
The torque data are for example in unit [dN·m]. Rheometry data exhibit for example a significant increase of the measured torque due to curing of the sample material. Rheometry projects require the raw torque data from a rotational rheometer in unit [dN·m].
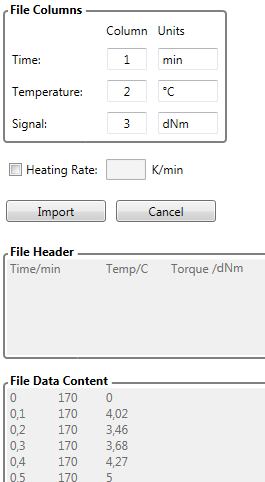
Arbitrary
Please write the number of columns for time, temperature and measured signal. The units for time is mostly [min], for temperature [°C]. For arbitrary data types you can set your Signal Name and Units during Import.
.
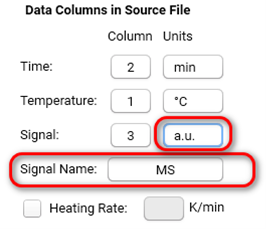
Please see details on the page Arbitrary Data Types.