Model-Free: Friedman Analysis
The Friedman analysis is an isoconversional method, where the measurements are analyzed for multiple conversion levels. At least two measurements are required.
The determination of the activation energy is using the points at the same conversion (0.01, 0.02, …, 0.99) from the measurements at different heating rates or different isothermal conditions. There is no assumption about the reaction type.
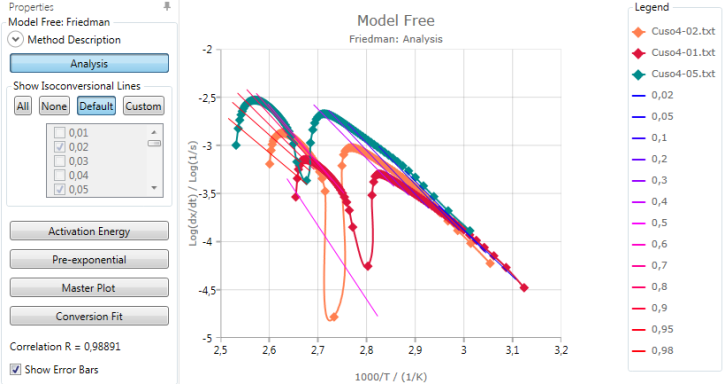
Analysis
Analysis shows a graphic of Log(ConversionRate) vs. inverse temperatures of the points at the same conversion. Linear fit curves are shown for each conversion value specified:
Any of these isoconversional lines can be shown by selecting All, None, Default or Custom:
Activation energy and pre-exponential results are found from the slope and intersect of these linear fits.
The calculated Correlation R is explained in section Statistics.
Activation Energy
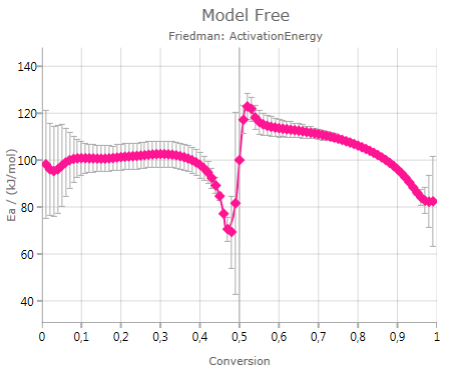
Pressing
![]()
shows the calculated activation energy including error bar – if the checkbox Show Error Bars is activated:
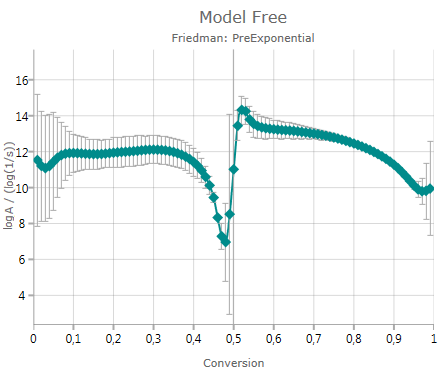
Pre-Exponential Factor
Pressing
![]()
shows the calculated pre-exponential including error bar – if activated:
The chart presents decimal logarithm of pre-exponential factor.
Master Plot
Pressing
![]()
shows the calculated ratio f(α)/f(0.5):
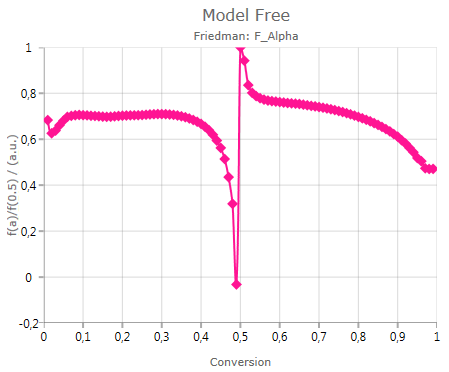
The ratio f(α)/f(0.5) is useful for the graphical estimation of the reaction type for single-step processes.
Conversion Fit
Pressing
![]()
shows experimental and simulated values, where the simulation is done based on the results of the Friedman analysis:
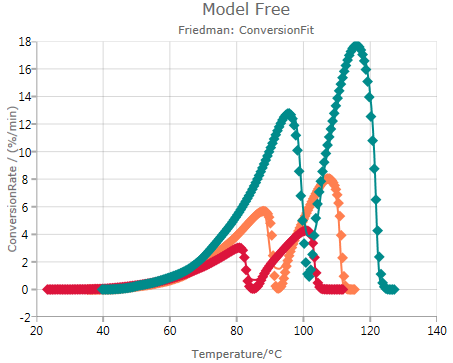
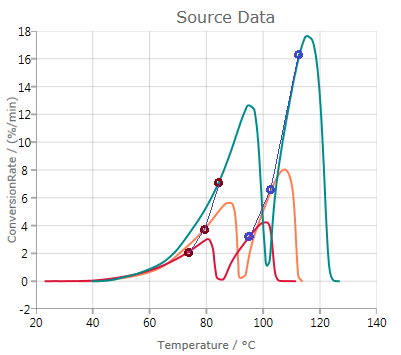
In this case, a good match between data and simulated values is observed. This indicates that the Friedman analysis is reliable in this case.
Advantages
Advantages of this method:
- for multiple-step reactions without parallel reaction steps
- each reaction point is evaluated
- suitable for dynamic and isothermal measurements
Disadvantages
Disadvantages of this method:
for parallel and independent reactions, Friedman gives the mean values of Ea