Baseline for Dilatometry (DIL) Data
In the case of DIL data, Prepare Data includes also the possibility to define an interpolated baseline that is subtracted from the data. There are four possibilities:
Baseline: None
None means that no baseline is applied.
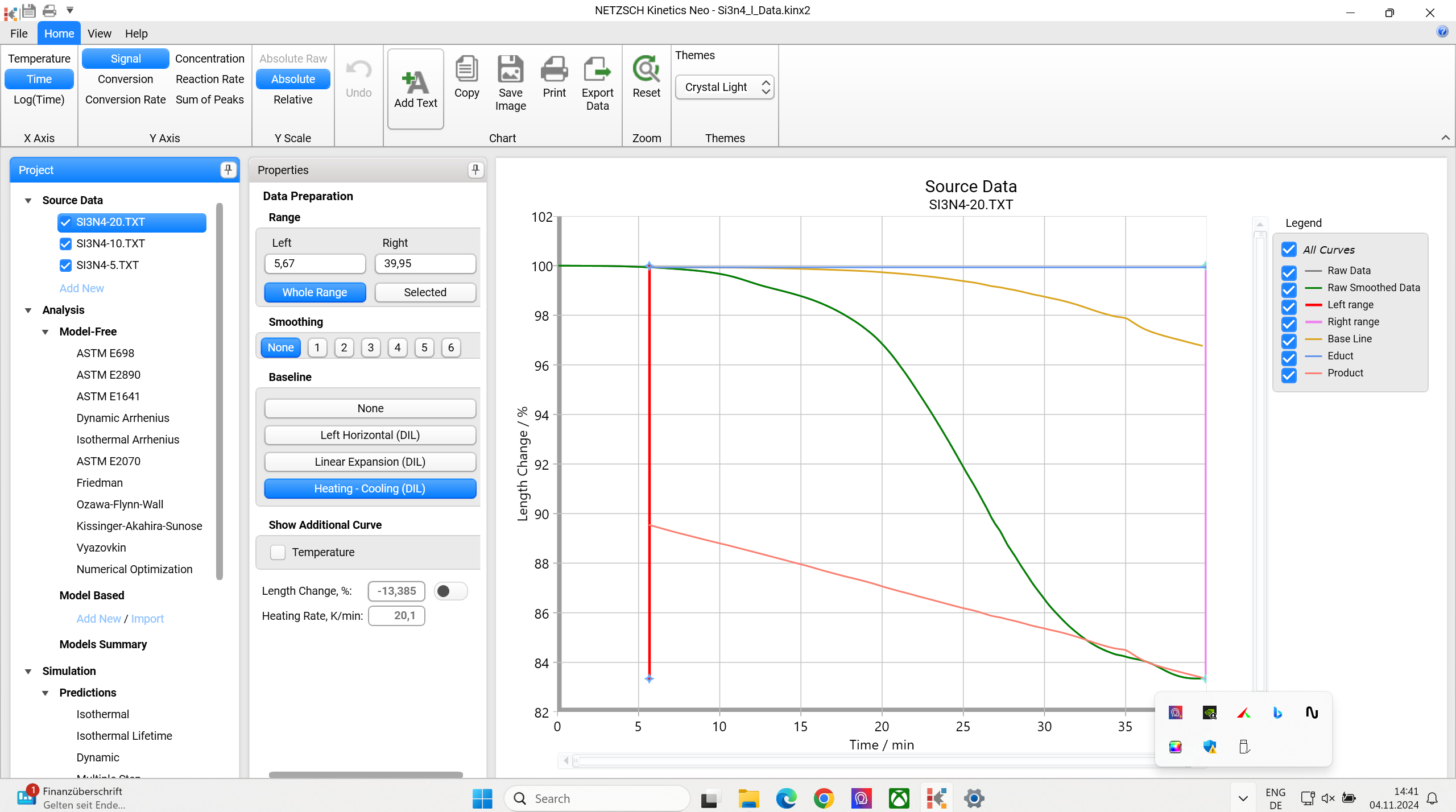
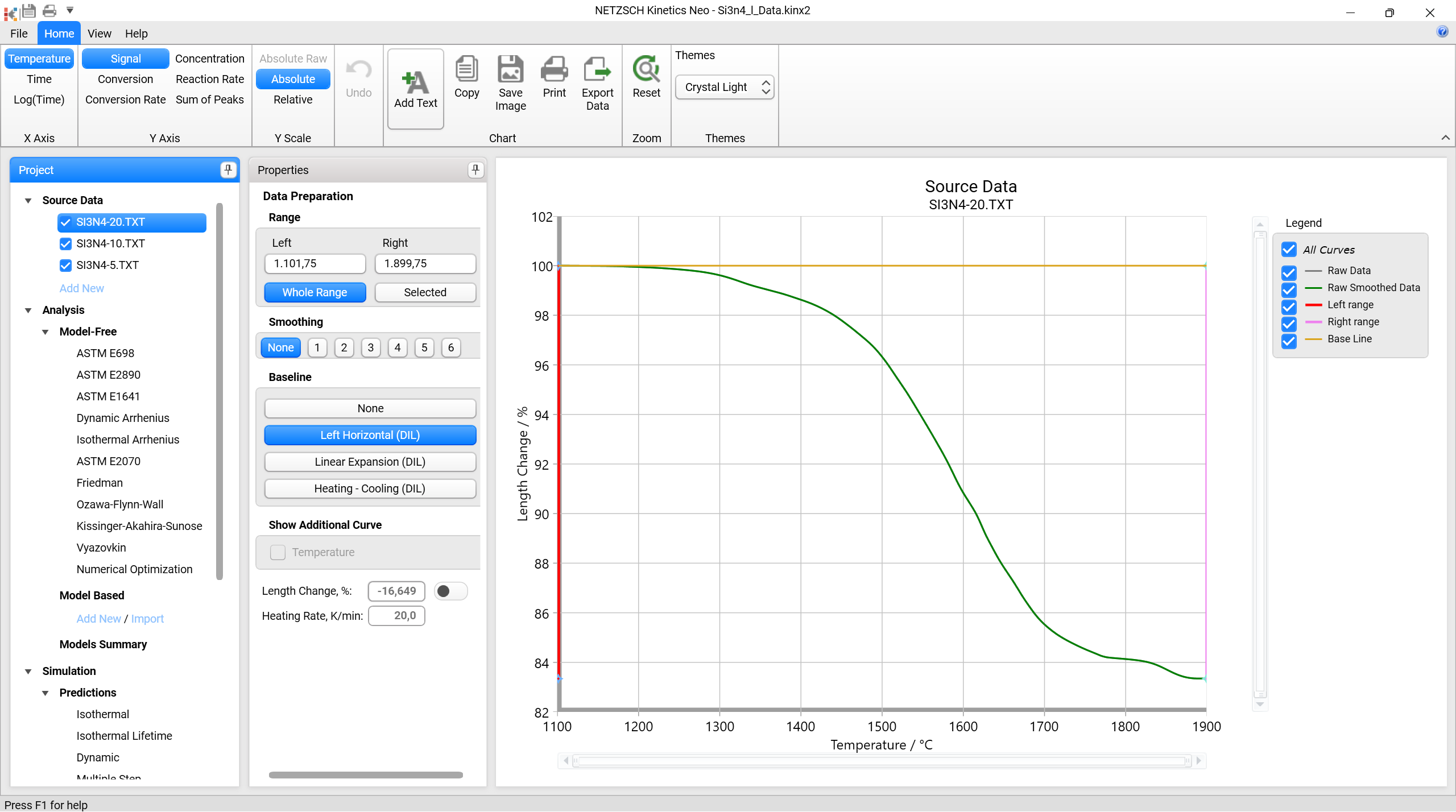
Baseline: Left Horizontal (DIL)
Left Horizontal (DIL) uses a horizontal baseline where the constant value of the baseline is the data point at the left cursor:
Baseline: Linear Expansion (DIL)
Linear Expansion (DIL) uses a thermal expansion curve as baseline where the constant expansion coefficient is determined at the left cursor. The baseline reflects the thermal expansion during the heating segment, a constant length during the isothermal segment and the thermal contraction during the cooling segment .
Example in temperature-dependent view:
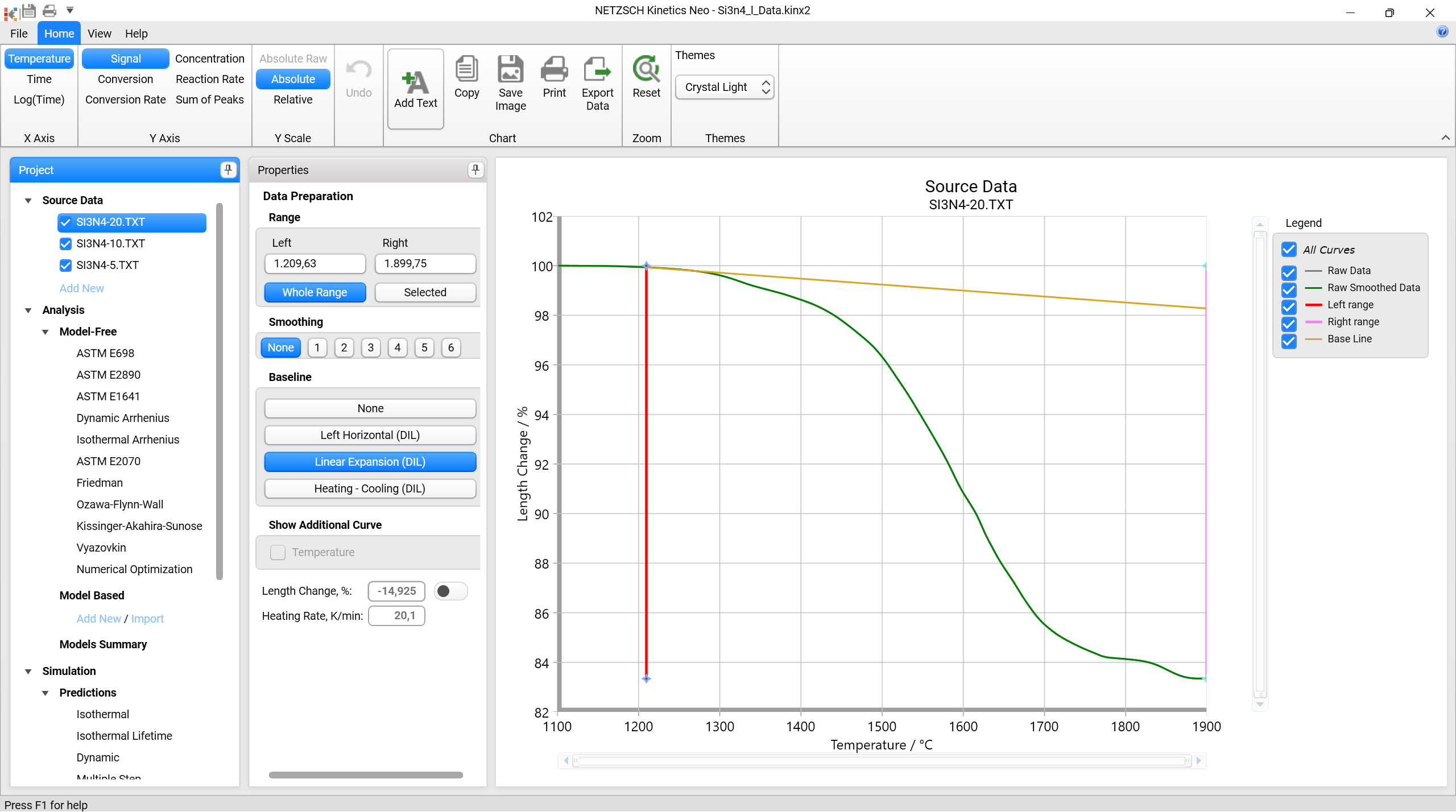
.
Baseline: Heating-Cooling (DIL)
Heating-Cooling (DIL), which is a further development of Linear Expansion (DIL) baseline, uses a thermal expansion curve as baseline, where the expansion coefficient has different values before and after the sintering. This baseline type can only be defined in time-dependent view. Furthermore, a heating and a cooling segment are required. At the left cursor, the expansion coefficient αe of the educt is determined; at the right cursor the expansion coefficient αp of the product; these calculated expansion curves of the educt and of the product are shown in the plot. The expansion coefficient of the baseline varies between αe and αpwhere the interpolation is calculated utilizing the deviation of the data from the expansion with αe to expansion with αp as a weight function.